Author: Editorial Staff
Alternet Systems Announces New Partnership Developments for Patented Lithium Technologies Tested in Cooperation With Nissan and Sanyo
UV Coating and Curing System for Lithium Ion Battery Ceramic Coated Anodes
Ossia Debuts Cota ‘Forever Battery’
How to Charge Li-Ion with a Parasitic Load
Contributed commentary by Isidor Buchmann, CEO & Founder, Cadex Electronics Inc.
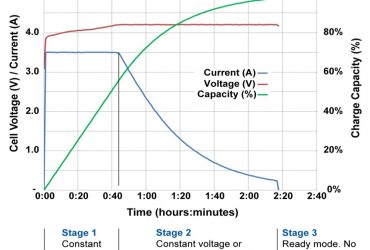
Charging a battery is simple but the complexity rises when a parasitic load is present during charge. Depending on battery chemistry, the charge process goes through several stages, and with lithium-ion Stage 1 consists of a constant current (CC) charge that brings the battery to roughly 70 percent state-of-charge (SoC). The cell reaches 4.20V/cell, a common voltage limit for Li-ion, after which Stage 2 continues by applying a constant voltage (CV) charge. The current begins to drop as the battery saturates. Full-charge is reached when the current decreases to typically 0.05C, which is one-twentieth of the rated ampere-hour. Li-ion cannot absorb overcharge and no charge is applied in Stage 3. Figure 1 illustrates typical voltage, current and capacity signatures of the CCCV charge. Read more about How to Charge Li-Ion with a Parasitic Load …